全部课程



【重磅】思科发布全新CCIE体系,再见了路由交换!
发布时间: 2019-06-14

思科厂商发布了最新CCIE认证体系重磅消息,R&S CCIE退出历史舞台,替代CCIE R&S的是:CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure(企业基础架构)。
新的认证将于2020年2月24日发布,当前认证截止日期是2020年2月23日!现有的认证仍有效,但如果在2月24日后获得认证,将获得新的认证和相关的证书,所以在学思科认证的小伙伴们,抓紧时间学习考试,新的一波认证来袭后,考题也随之更新。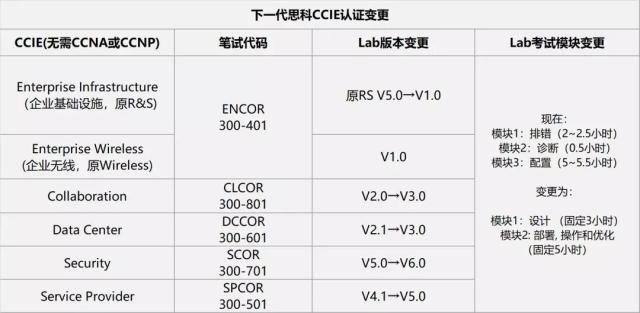
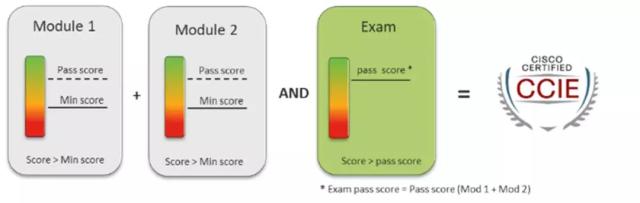
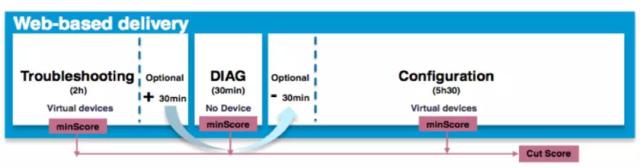
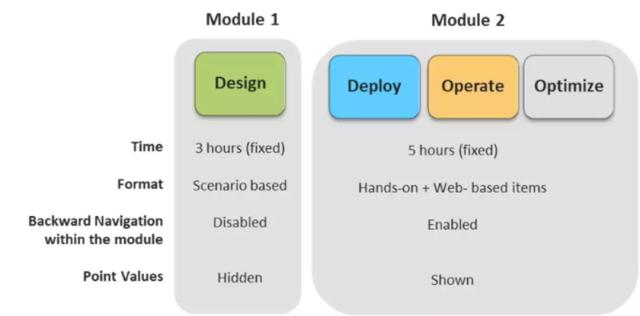
在LAB考试中,各个考试内容的框架下图所示:

附考试大纲:
1. Network Infrastructure (30%) 1.1 Switched campus 1.1.a Switch administration 1.1.a i Managing MAC address table 1.1.a ii Errdisable recovery 1.1.a iii L2 MTU 1.1.b Layer 2 protocols 1.1.b i CDP, LLDP 1.1.b ii UDLD 1.1.c VLAN technologies 1.1.c i Access ports 1.1.c ii Trunk ports (802.1q) 1.1.c iii Native VLAN 1.1.c iv Manual pruning 1.1.c v VLAN database 1.1.c vi Normal and extended VLANs 1.1.c vii Voice VLAN 1.1.c viii VTP 1.1.d EtherChannel 1.1.d i LACP, manual 1.1.d ii Layer 2, layer 3 1.1.d iii Load balancing 1.1.d iv EtherChannel misconfiguration guard 1.1.e Spanning-Tree 1.1.e i PVST+, Rapid PVST+, MST 1.1.e ii Switch priority, port priority, path cost, STP timers 1.1.e iii PortFast, BPDU Guard, BPDU Filter 1.1.e iv Loop Guard, Root Guard 1.2 Routing Concepts 1.2.a Administrative distance 1.2.b VRF-lite 1.2.c Static routing 1.2.d Policy-based routing 1.2.e VRF aware routing with any routing protocol 1.2.f Filtering with any routing protocol 1.2.g Manual summarization with any routing protocol 1.2.h Redistribution between any pair of routing protocols 1.2.i Routing protocol authentication 1.2.j Bidirectional Forwarding Detection 1.3 EIGRP 1.3.a Adjacencies 1.3.b Best path selection 1.3.b i RD, FD, FC, successor, feasible successor 1.3.b ii Classic metric and wide metric 1.3.c Operations 1.3.c i General operations 1.3.c ii Topology table 1.3.c iii Packet types 1.3.c iv Stuck In Active 1.3.c v Graceful shutdown 1.3.d EIGRP load-balancing 1.3.d i Equal-cost 1.3.d ii Unequal-cost 1.3.d iii Add-path 1.3.e EIGRP named mode 1.3.f Optimization, convergence and scalability 1.3.f i Fast convergence requirements 1.3.f ii Query propagation boundar 1.4 OSPF (v2 and v3) 1.4.a Adjacencies 1.4.b Network types, area types 1.4.c Path preference 1.4.d Operations 1.4.d i General operations 1.4.d ii Graceful shutdown 1.4.d iii GTSM (Generic TTL Security Mechanism) 1.4.e Optimization, convergence and scalability 1.4.e i Metrics 1.4.e ii LSA throttling, SPF tuning, fast hello 1.4.e iii LSA propagation control (area types) 1.4.e iv Stub router 1.4.e v Loop-free alternate 1.4.e vi Prefix suppression 1.5 BGP 1.5.a IBGP and EBGP peer relationships 1.5.a i Peer-group/update-group, template 1.5.a ii Active, passive 1.5.a iii Timers 1.5.a iv Dynamic neighbors 1.5.a v 4 Bytes AS number 1.5.a vi Private AS 1.5.b Path selection 1.5.b i Attributes 1.5.b ii Best path selection algorithm 1.5.b iii Load-balancing 1.5.c Routing policies 1.5.c i Attribute manipulation 1.5.c ii Conditional advertisement 1.5.c iii Outbound Route Filtering 1.5.c iv Standard and extended communities 1.5.c v Multi-homing 1.5.d AS path manipulations 1.5.d i Local AS, allowas- in, remove private as 1.5.d ii Prepend 1.5.d iii Regexp 1.5.e Convergence and scalability 1.5.e i Route reflector 1.5.e ii Aggregation, AS set 1.5.f Other BGP features 1.5.f i Multipath, add-path 1.5.f ii Soft reconfiguration, route refresh 1.6 Multicast 1.6.a Layer 2 multicast 1.6.a i IGMPv2, IGMPv3 1.6.a ii IGMP Snooping, PIM Snooping 1.6.a iii IGMP Querier 1.6.a iv IGMP Filter 1.6.a v MLD 1.6.b Reverse path forwarding check 1.6.c PIM 1.6.c i Sparse Mode 1.6.c ii Static RP, BSR, AutoRP 1.6.c iii Group to RP Mapping 1.6.c iv Bidirectional PIM 1.6.c v Source-Specific Multicast 1.6.c vi Multicast boundary, RP announcement filter 1.6.c vii PIMv6 Anycast RP 1.6.c viii IPv4 Anycast RP using MSDP 1.6.c ix Multicast multipath 2. Software Defined Infrastructure (25%) 2.1 Cisco SD Access 2.1.a Design a Cisco SD Access solution 2.1.a i Underlay network (ISIS, manual/PnP) 2.1.a ii Overlay fabric design (LISP, VXLAN, Cisco TrustSec) 2.1.a iii Fabric domains (single-site and multi-site) 2.1.b Cisco SD Access deployment 2.1.b i Cisco DNA Center device discovery and device management 2.1.b ii Add edge node devices to an existing fabric 2.1.b iii Host onboarding (wired endpoints only) 2.1.b iv Fabric border handoff 2.1.c Segmentation 2.1.c i Macro-level segmentation using VNs 2.1.c ii Micro-level segmentation using SGTs (using Cisco ISE) 2.1.d Assurance 2.1.d i Network and client health (360) 2.1.d ii Monitoring and troubleshooting 2.2 Cisco SD-WAN 2.2.a Design a Cisco SD-WAN solution 2.2.a i Orchestration plane (vBond, NAT) 2.2.a ii Management plane (vManage) 2.2.a iii Control plane (vSmart, OMP) 2.2.a iv Data plane (vEdge/cEdge) 2.2.b WAN edge deployment 2.2.b i Onboarding new edge routers 2.2.b ii Orchestration with zero-touch provisioning/Plug-And-Play 2.2.b iii OMP 2.2.b iv TLOC 2.2.c Configuration templates 2.2.d Localized policies (only QoS) 2.2.e Centralized policies 2.2.e i Application Aware Routing 2.2.e ii Topologies 3. Transport Technologies and Solutions (15%) 3.1 MPLS 3.1.a Operations 3.1.a i Label stack, LSR, LSP 3.1.a ii LDP 3.1.a iii MPLS ping, MPLS traceroute 3.1.b L3VPN 3.1.b i PE-CE routing 3.1.b ii MP-BGP VPNv4 -v6 3.1.b iii Extranet (route leaking) 3.2 DMVPN 3.2.a Troubleshoot DMVPN phase 3 with dual-hub 3.2.a i NHRP 3.2.a ii IPsec/IKEv2 using preshared key 3.2.a iii Per-Tunnel QoS 3.2.b Identify use-cases for FlexVPN 3.2.b i Site-to-site, Server, Client, Spoke-to-Spoke 3.2.b ii IPsec/IKEv2 using preshared key 3.2.b iii MPLS over FlexVPN 4. Infrastructure Security and Services (15%) 4.1 Device Security on Cisco IOS XE 4.1.a Control plane policing and protection 4.1.b AAA 4.2 Network Security 4.2.a Switch security features 4.2.a i VACL, PACL 4.2.a ii Storm control 4.2.a iii DHCP snooping, DHCP option 82 4.2.a iv IP Source Guard 4.2.a v Dynamic ARP inspection 4.2.a vi Port-security 4.2.a vii Private VLAN 4.2.b Router security features 4.2.b i IPv6 Traffic filters 4.2.b ii IPv4 Access Control Lists 4.2.b iii Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding 4.2.c IPv6 First Hop Security features 4.2.c i RA guard 4.2.c ii DHCP guard 4.2.c iii Binding table 4.2.c iv Device tracking 4.2.c v ND inspection/snooping 4.2.c vi Source guard 4.2.d IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Authentication 4.2.d i Device roles, port states 4.2.d ii Authentication process 4.2.d iii Host modes 4.3 System Management 4.3.a Device management 4.3.a i Console and VTY 4.3.a ii SSH, SCP 4.3.a iii RESTCONF, NETCONF 4.3.b SNMP 4.3.b i v2c 4.3.b ii v3 4.3.c Logging 4.3.c i Local logging, syslog, debugs, conditional debugs 4.3.c ii Timestamps 4.4 Quality of Service 4.4.a End to end L3 QoS using MQC 4.4.a i DiffServ 4.4.a ii CoS and DSCP Mapping 4.4.a iii Classification 4.4.a iv Network Based Application Recognition (NBAR) 4.4.a v Marking using IP Precedence, DSCP, CoS 4.4.a vi Policing, shaping 4.4.a vii Congestion management and avoidance 4.4.a viii HQoS, Sub-rate Ethernet Link 4.5 Network Services 4.5.a First-Hop Redundancy protocols 4.5.a i HSRP, GLBP, VRRP 4.5.a ii Redundancy using IPv6 RS/RA 4.5.b Network Time Protocol 4.5.b i Master, client 4.5.b ii Authentication 4.5.c DHCP on Cisco IOS 4.5.c i Client, server, relay 4.5.c ii Options 4.5.c iii SLAAC/DHCPv6 interaction 4.5.c iv Stateful, stateless DHCPv6 4.5.c v DHCPv6 prefix delegation 4.5.d IPv4 Network Address Translation 4.5.d i Static NAT, PAT 4.5.d ii Dynamic NAT, PAT 4.5.d iii Policy-based NAT, PAT 4.5.d iv VRF aware NAT, PAT 4.5.d v VASI 4.6 Network optimization 4.6.a IP SLA 4.6.a i ICMP probes 4.6.a ii UDP probes 4.6.a iii TCP probes 4.6.b Tracking object 4.6.c Flexible netflow 4.7 Network operations 4.7.a Traffic capture 4.7.a i SPAN 4.7.a ii RSPAN 4.7.a iii ERSPAN 4.7.a iv Embedded packet capture 4.7.b Cisco IOS-XE Troubleshooting tools 4.7.b i Packet-tracer 4.7.b ii Conditional debugger (debug platform condition) 5. Infrastructure Automation and Programmability (15%) 5.1 Data encoding formats 5.1.a JSON 5.1.b XML 5.2 Automation and scripting 5.2.a EEM applets 5.2.b Guest shell 5.2.b i Linux environment 5.2.b ii CLI Python module 5.2.b iii EEM Python module 5.3 Programmability 5.3.a Interaction with vManage API 5.3.a i Python requests library or Postman 5.3.a ii Monitoring endpoints 5.3.a iii Configuration endpoints 5.3.b Interaction with Cisco DNA Center API 5.3.b i HTTP request (GET, PUT, POST) via Python requests library or Postman 5.3.c Interaction with Cisco IOS XE API 5.3.c i Via NETCONF/YANG using Python ncclient library 5.3.c ii Via RESTCONF/YANG using Python requests library or Postman 5.3.d Deploy and verify model-driven telemetry 5.3.d i Configure on-change subscription using gRPC |
上一篇: 恭喜腾科学员通过OCM大师认证!